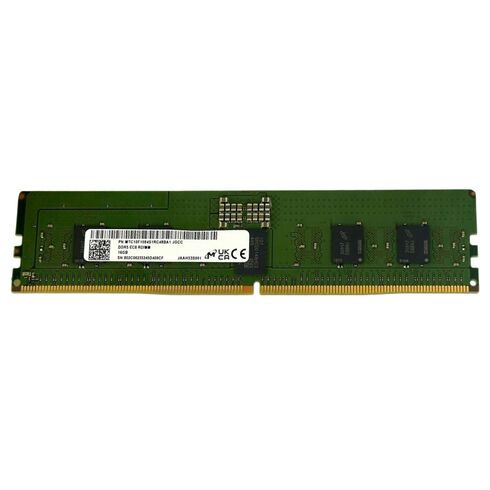
MTC10F1084S1RC64B Micron 16GB DDR5 6400MHz PC5-51200 288-Pin DIMM Memory Kit
- — Free Ground Shipping
- — Min. 6-month Replacement Warranty
- — Genuine/Authentic Products
- — Easy Return and Exchange
- — Different Payment Methods
- — Best Price
- — We Guarantee Price Matching
- — Tax-Exempt Facilities
- — 24/7 Live Chat, Phone Support
- — Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and Amex
- — JCB, Diners Club, UnionPay
- — PayPal, ACH/Bank Transfer (11% Off)
- — Apple Pay, Amazon Pay, Google Pay
- — Buy Now, Pay Later - Affirm, Afterpay
- — GOV/EDU/Institutions PO's Accepted
- — Invoices
- — Deliver Anywhere
- — Express Delivery in the USA and Worldwide
- — Ship to -APO -FPO
- — For USA - Free Ground Shipping
- — Worldwide - from $30
Product Overview of Micron 16GB DDR5 Memory Kit
The Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B 16GB DDR5 memory module represents a significant leap forward in server and high-performance computing memory technology. Engineered for next-generation data centers, enterprise servers, and workstations, this module combines Micron's industry-leading DRAM fabrication with the robust features of the DDR5 standard.
General Information
- Manufacturer: Micron
- Part Number: MTC10F1084S1RC64B
- Product Type: 16GB DDR5 Memory Module
Technical Information
- Technology: DDR5 SDRAM
- Module Size: 16GB
- Transfer Speed: 5600MHz
- Pin Count: 288-pin
- Bus Standard: PC5-51200
Performance Attributes
- Error Handling: Registered ECC for advanced data integrity
- Latency: CL46
- Clock Frequency: 3200MHz
- Voltage Requirement: 1.1V
Structural Design
- Rank Configuration: Single Rank (1Rx8)
- Form Factor: Compact dimensions of 7.5 × 11 × 1 mm
Key Highlights
- Optimized for high-bandwidth applications and multitasking environments
- ECC support ensures stability in mission-critical systems
- Low operating voltage enhances energy efficiency
- Precision-built Micron design guarantees compatibility with modern server platforms
Understanding the Micron 16GB DDR5 Memory Kit
The Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B represents a significant leap forward in server and high-performance workstation memory technology. As a 16GB DDR5 module operating at 6400MT/s (Megatransfers per second), it is engineered for systems demanding exceptional data integrity, bandwidth, and power efficiency. This module falls into the critical category of ECC (Error-Correcting Code) Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs), a mainstay for enterprise servers, data centers, and mission-critical computing environments. Its specifications—PC5-51200, 288-pin, 1.1V, Single Rank—provide a blueprint for its performance characteristics and compatibility. This category of memory is designed not for casual consumer use but for the backbone of modern digital infrastructure, where uptime, accuracy, and throughput are non-negotiable.
Key Specifications
At its core, the MTC10F1084S1RC64B is defined by a precise set of technical parameters that dictate its performance and application. Understanding each element is key to selecting the right memory for a system build or upgrade.
Capacity and Architecture: 16GB Single Rank
The 16GB capacity offers a balance between density and performance for many server configurations. The "Single Rank" designation indicates how the memory chips are organized on the module. A single rank module presents one set of 64-bit data blocks (72-bit with ECC) to the memory controller. Compared to dual-rank modules of the same capacity, single rank modules can sometimes allow for higher clock speeds or lower loading on the memory controller, which can be advantageous when populating many channels or seeking peak transfer rates.
Rank Organization
The single-rank design of this Micron module means all DRAM chips are accessed simultaneously for a full data word. This structure can reduce the electrical load on the memory controller compared to accessing a dual-rank module, potentially enabling easier signal integrity management at high speeds like 6400MT/s. For system integrators, this means optimized performance in channels that are fully populated, allowing the memory controller to maintain high frequencies with stability.
The DDR5 Revolution: 6400MHz PC5-51200
DDR5 memory, the successor to DDR4, introduces fundamental architectural improvements. The MTC10F1084S1RC64B operates at a data rate of 6400 Megatransfers per second, which is often referred to as 6400MHz. The corresponding bandwidth classification is PC5-51200. The "PC5" denotes DDR5, and "51200" refers to the peak theoretical bandwidth in MB/s per module. Calculated as (6400 MT/s * 64 bits / 8 bits per byte), this yields 51,200 MB/s of bandwidth, a substantial increase over previous-generation DDR4 modules.
Dual Sub-Channel Architecture
A key innovation in DDR5 is the division of each DIMM into two independent 32-bit (40-bit with ECC) addressable sub-channels. While this Micron module is a single-rank part, it still benefits from this DDR5 architectural shift. This design allows for finer-grained memory access, reducing latency and improving concurrency compared to the single 64-bit channel of DDR4. For the memory controller, this means more efficient command scheduling and data handling.
On-Die ECC (Error Correction Code)
Beyond the module-level ECC, DDR5 introduces On-Die ECC. This is an additional, separate layer of error correction that operates within each individual DRAM chip on the module. It corrects minor bit errors internally before data is sent to the module's buffer chip. This feature enhances data reliability at the chip level, reducing the burden on the main ECC system and contributing to overall system longevity and data integrity.
The Critical Role of ECC and Registered Buffers
The "ECC Registered" in the module's description points to two of its most crucial features for enterprise stability. These are not mere performance add-ons but foundational requirements for reliable server operation.
ECC: Error-Correcting Code Memory
ECC memory includes extra bits (8 bits for every 64 bits of data in a standard configuration) to store an encrypted code. When data is written to memory, the ECC code is calculated and stored. Upon readback, the code is recalculated and compared. If a single-bit error (a flipped 1 or 0) is detected, the ECC circuitry corrects it instantly and transparently. It can also detect, though not always correct, multi-bit errors. For servers running databases, financial transactions, scientific computations, or virtualization, this hardware-level error correction is essential to prevent silent data corruption, system crashes, and unpredictable behavior.
Comparing ECC to Non-ECC Memory
Non-ECC (unbuffered) consumer memory has no such protection. A cosmic ray or electrical interference causing a bit flip can corrupt data, lead to application errors, or cause a system halt. In an enterprise setting, the risk and cost of such events are unacceptable. The Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B's ECC feature provides a fundamental layer of hardware resilience, ensuring data remains accurate as it resides in system memory.
Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) and the Role of the RCD
The "Registered" component refers to the presence of a register clock driver (RCD) chip on the module. This chip sits between the system's memory controller and the DRAM chips. It buffers the command, address, and clock signals, reducing the electrical load on the memory controller. This allows a server motherboard to support a much greater number of memory modules—often scaling to multiple terabytes—without overwhelming the controller's driving capability.
Stability at Scale: The RDIMM Advantage
While RDIMMs introduce a slight, typically one-clock-cycle, latency penalty due to signal buffering, the trade-off is immense stability and capacity scaling. This makes the Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B an ideal choice for multi-socket servers and densely populated memory configurations. The RCD ensures clean, stable signals to all DRAM chips, which is paramount for maintaining data integrity at high speeds like 6400MT/s across a large memory array.
1.1V and 288-Pin Form Factor
The move to DDR5 brings tangible improvements in power efficiency and physical interface, both embodied in this module's design.
Enhanced Power Efficiency at 1.1V
Operating at a nominal voltage of 1.1V, this DDR5 module consumes less power than a typical DDR4 module operating at 1.2V. This reduction directly lowers the power consumption and heat output of the memory subsystem. In a data center with thousands of servers, even a 0.1V reduction per module translates to significant operational cost savings and a reduced thermal load on cooling systems. The module also features a more advanced power management integrated circuit (PMIC) on the DIMM itself, moving voltage regulation from the motherboard to the module for better signal integrity and noise mitigation.
The On-Module PMIC (Power Management Integrated Circuit)
A distinct feature of DDR5 is the relocation of power management. The Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B includes its own PMIC. This chip provides more stable and cleaner power to the DRAM chips by regulating the 12V supply from the server power rail down to the required voltages (VDD, VDDQ, etc.). This reduces power supply noise, improves voltage tolerances, and enhances overall module stability, especially during power state transitions, which is critical for server reliability.
The 288-Pin DIMM Interface
The MTC10F1084S1RC64B utilizes a 288-pin edge connector, which is physically different from DDR4's 288-pin design (the key notch is in a different location to prevent insertion into an incompatible slot). The pinout supports the enhanced feature set of DDR5, including the two sub-channels and additional power and ground pins for the on-DIMM PMIC. This physical design ensures the module can only be installed in a motherboard with a DDR5-capable memory slot and chipset, guaranteeing correct electrical and logical compatibility.
Compatibility and Target Applications
This memory module is not designed for consumer desktop platforms. Its specific characteristics define a clear set of compatible systems and ideal use cases.
Ideal Workloads and Deployment Scenarios
The combination of high bandwidth (6400MT/s), robust ECC protection, and registered stability makes this module suitable for a wide array of demanding compute tasks.
In-Memory Databases and Analytics
Platforms such as SAP HANA, Redis, or Apache Spark thrive on fast memory access. The 51.2 GB/s bandwidth of this module accelerates data processing, while ECC ensures the analytical results are computed accurately, which is vital for business intelligence and real-time analytics.
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
Computational fluid dynamics, financial modeling, and genomic sequencing involve massive datasets and prolonged calculations. The integrity offered by ECC is non-negotiable, as a single bit-flip could invalidate days of computation. The high bandwidth also speeds up time-to-solution.
Enterprise Storage and Backup Appliances
Modern storage area networks (SAN) and network-attached storage (NAS) appliances use large amounts of RAM for caching and metadata management. ECC memory is a standard requirement here to prevent data corruption at the caching layer, ensuring data written to or read from storage is perfectly accurate.
Performance Considerations
While speed (6400MT/s) is a headline figure, the module's performance is also governed by its latency timings and its ability to operate in multi-channel configurations.
Latency Timings in ECC RDIMMs
Like all DDR memory, this module operates with a set of timing numbers (e.g., CL40-40-40). These represent the latency in clock cycles for various operations. ECC RDIMMs, due to the buffering of signals, often have slightly higher CAS latencies than unbuffered desktop memory. However, the immense bandwidth and stability advantages far outweigh this minor cycle penalty in server workloads, which are typically throughput-sensitive rather than latency-sensitive. Furthermore, the improved efficiency of DDR5's architecture helps mitigate absolute latency in nanoseconds compared to DDR4.
The Impact of Speed and Latency on Throughput
At 6400MT/s, even with a CAS Latency (CL) of 40, the absolute time to access the first piece of data is calculable. More importantly for servers, the sustained bandwidth after the initial access is exceptional. The combination of high data rate, dual sub-channels, and the efficiency of registered operation provides a consistent, high-throughput pipeline for data-intensive applications.
Multi-Channel and Interleaving Advantages
Server CPUs feature multiple memory channels (often 8 or 12). The Micron MTC10F1084S1RC64B is designed to be installed in matched sets per channel to enable multi-channel interleaving. This technique spreads memory accesses across multiple modules simultaneously, dramatically increasing aggregate system bandwidth far beyond the 51.2 GB/s of a single module. For optimal performance, these modules should be installed following the server manufacturer's population guidelines for balanced channel loading.