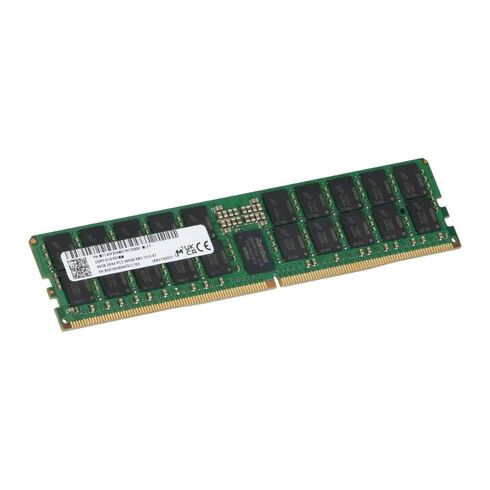
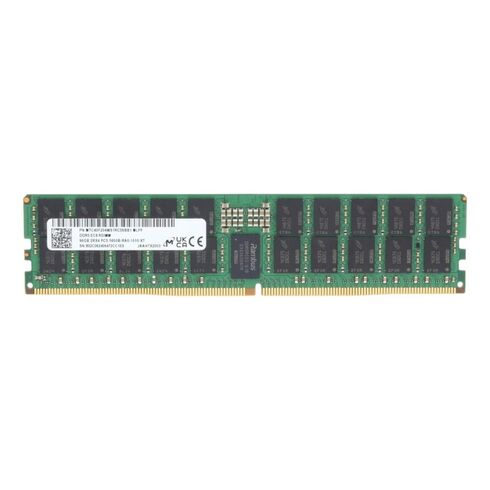
Micron MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 96GB DDR5 Dual Rank PC5-51200 Memory.
- — Free Ground Shipping
- — Min. 6-month Replacement Warranty
- — Genuine/Authentic Products
- — Easy Return and Exchange
- — Different Payment Methods
- — Best Price
- — We Guarantee Price Matching
- — Tax-Exempt Facilities
- — 24/7 Live Chat, Phone Support
- — Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and Amex
- — JCB, Diners Club, UnionPay
- — PayPal, ACH/Bank Transfer (11% Off)
- — Apple Pay, Amazon Pay, Google Pay
- — Buy Now, Pay Later - Affirm, Afterpay
- — GOV/EDU/Institutions PO's Accepted
- — Invoices
- — Deliver Anywhere
- — Express Delivery in the USA and Worldwide
- — Ship to -APO -FPO
- — For USA - Free Ground Shipping
- — Worldwide - from $30
Same product also available in:
| SKU/MPN | Warranty | Price | Condition | You save |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 | 1 Year Warranty | $5,520.00 | New Sealed in Box (NIB) | You save: $1,932.00 (26%) |
| MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 | 1 Year Warranty | $3,499.00 | New (System) Pull | You save: $1,224.65 (26%) |
Micron 96GB DDR5 RDIMM Memory Module
The Micron MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 is a high-capacity, high-performance DDR5 registered memory module engineered for data-intensive applications and enterprise-grade systems. Designed for reliability and speed, this 96GB ECC RDIMM ensures exceptional data integrity and operational efficiency.
Key Features
- Massive 96GB memory capacity for demanding workloads
- High-speed 6400MHz (PC5-51200) data rate
- Error-Correcting Code (ECC) support for robust data accuracy
- Registered DIMM for improved stability in server environments
- Dual Rank x8 configuration for optimized performance
- Low operating voltage of 1.1V for energy efficiency
Manufacturer Details
Brand Information
- Brand: Micron Technology
- Manufacturer Part Number: MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2
- Product Identifier: 96GB DDR5 SDRAM Module
Technical Specifications
Memory Configuration
- Installed Memory: 96GB per module
- Module Count: 1 x 96GB
- Memory Type: DDR5 SDRAM
- Speed Rating: 6400MHz (PC5-51200)
- CAS Latency: CL52
- Signal Type: Registered (RDIMM)
Reliability and Performance
- Error Correction: ECC (Error-Correcting Code)
- Rank Structure: Dual Rank x8
- Voltage: 1.1V
Form Factor and Compatibility
Physical Design
- Pin Layout: 288-pin RDIMM
- Form Factor: Registered DIMM
Shipping Information
- Package Dimensions: 1.00 in (H) x 6.75 in (D)
- Weight: 0.20 lbs
Ideal Applications
- High-performance computing (HPC)
- Enterprise servers and data centers
- Virtualization and cloud workloads
- AI and machine learning infrastructures
Advanced Memory Architecture
- Improved bandwidth and reduced latency
- Greater memory density for scalability
- Optimized power efficiency with lower voltage
Enterprise-Grade Reliability
- ECC technology for accurate data processing
- Registered memory design for maximum uptime
- Backed by Micron’s industry-leading manufacturing standards
Future-Ready Performance
- Designed for next-gen server platforms
- Supports high-throughput applications and workloads
Micron MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 96GB DDR5 RDIMM
The Micron MTC40F204WS1RC64BB2 96GB DDR5 6400MHz Dual Rank PC5-51200 ECC Registered 288-pin RDIMM is a high-capacity, high-bandwidth registered memory module engineered for modern servers, workstations, and mission-critical systems. Built using Micron’s advanced DRAM process and rigorous quality controls, this RDIMM combines large memory density with ECC (Error Correcting Code) and register-buffered design to deliver exceptional reliability, data integrity, and sustained throughput for virtualization, in-memory databases, analytics, and virtualization-heavy infrastructures. This category description explores the technical characteristics, practical applications, compatibility considerations, thermal and power behavior, and selection guidance for systems administrators, procurement teams, and technically-minded buyers.
Key specifications and what they mean
Core electrical and mechanical attributes
The module conforms to the industry-standard 288-pin RDIMM mechanical form factor and adheres to JEDEC DDR5 specifications. Important trade names and technical numbers that buyers should recognize include:
- Capacity: 96GB per module — high-density option for large-memory builds.
- Memory type: DDR5 SDRAM — next-generation memory offering higher bandwidth and improved power efficiency versus DDR4.
- Speed (data rate): 6400 MT/s (megatransfers per second) — listed commercially as DDR5-6400; raw theoretical bandwidth approximates the PC5-51200 class (51200 MB/s per module in peak sequential transfer scenarios).
- Module designation: PC5-51200 — indicates peak theoretical transfer rate class for marketing and compatibility checks.
- Organization: Dual Rank — two logical ranks per module, which can affect memory channel utilization and capacity per channel.
- Error correction: ECC Registered — on-chip ECC plus register buffer; corrects single-bit errors and detects multi-bit errors to protect data integrity.
- Pin count: 288-pin RDIMM — standard modern server socket requiring RDIMM support on the motherboard or server platform.
JEDEC compliance and latency indicators
JEDEC-standardized timing, voltage, and training procedures ensure the module can be used across certified server families. DDR5 introduces on-die ECC and improved bank-group architectures; the Micron RDIMM will carry a specific CAS latency (CL) and command timing profile that system BIOS translates into actual operational timings. When planning memory mixes, prioritize modules with compatible JEDEC timing ranges and BIOS/firmware support to avoid fallback to lower speeds.
Performance characteristics and real-world throughput
Bandwidth, concurrency, and multi-socket behavior
DDR5-6400 provides substantially higher bandwidth per channel than DDR4-3200 and earlier generations. In multi-socket servers, aggregated system memory bandwidth scales with the number of channels and installed modules. A 96GB dual-rank RDIMM typically offers:
- High sustained throughput for sequential and streaming workloads such as large-scale analytics, media processing, and scientific simulations.
- Enhanced memory concurrency for many-threaded server applications — ideal for database caching layers, large in-memory key-value stores, and big-data node tasks.
- When combined with CPUs that support DDR5-6400, it minimizes platform-induced bottlenecks and reduces memory-bound stalls for data-intensive tasks.
Latency versus bandwidth trade-offs
Dual Rank modules can introduce a slight increase in nominal latency compared to single-rank modules due to rank switching, but the larger capacity and increased row-buffer locality typically outweigh that cost for capacity-heavy workloads. For latency-sensitive applications, test both single- and dual-rank configurations under realistic load; in many database and virtualization scenarios, the net performance climbs because more working set fits in RAM, reducing higher-latency storage accesses.
Reliability, error correction, and data integrity
ECC Registered design explained
ECC Registered RDIMMs blend two key features that enterprise customers require:
- ECC (Error Correcting Code): Detects and corrects single-bit errors and detects multi-bit errors, significantly lowering the risk of silent data corruption.
- Registered (buffered) interface: Uses a register to buffer control and address signals between the memory controller and DRAM devices, improving signal integrity on systems with many DIMMs per channel and enabling higher DIMM population densities.
The combined effect is predictable behavior under sustained loads and reduced error rates in enterprise deployments. Micron modules undergo burn-in, production-level screening, and post-manufacturing tests that target retention, timing margins, and thermal stress.
MTBF, burn-in, and manufacture traceability
Micron and other reputable DRAM manufacturers publish manufacturing test details, screening processes, and often provide mean time between failures (MTBF) estimates or reliability metrics for enterprise product families. Buyers should request lot traceability and access to warranty and RMA processes when procuring in bulk for data center rollout.
Use cases and recommended workloads
Virtualization and cloud hosting environments
Virtual machine density is directly correlated with available physical memory. A 96GB RDIMM is perfect for hypervisor hosts that must run many medium-sized VMs or fewer large VMs with big in-memory footprints. Key benefits include:
- Improved VM consolidation ratios.
- Reduced swapping to disk under peak loads.
- Better QOS for latency-sensitive guest workloads due to local memory availability.
Databases, in-memory caching, and analytics
In-memory databases and cache tiers (Redis, Memcached, SAP HANA-style in-memory analytics) benefit from both the capacity and the bandwidth of DDR5-6400 RDIMMs. Large working sets remain resident in RAM, trimming backend storage I/O and delivering predictable query latency under heavy concurrency.
High-performance computing (HPC) and scientific simulations
Scientific simulations and modeling tasks leverage high memory bandwidth and ample capacity for mesh state, particle systems, and large matrix computations. Dual-rank architectures can increase effective throughput in memory-bound kernels that benefit from rank interleaving and higher row-buffer hits.
Enterprise applications and virtualization platforms
Enterprise ERP systems, virtualization platforms, container orchestration nodes, and engineering workstations that require large address spaces are natural fits for 96GB RDIMMs. They are especially useful in servers running:
- Large-scale Java application servers (with big JVM heaps)
- Container orchestration masters and heavy worker nodes
- Software-defined storage controllers and caching tiers
Compatibility and platform considerations
Motherboard and CPU support
Before purchasing Micron 96GB DDR5 RDIMMs, verify the following platform details:
- CPU memory controller compatibility with DDR5 speeds (6400 MT/s) and registered DIMMs.
- Motherboard firmware/BIOS support for high-density RDIMMs and dual rank configurations.
- Maximum supported per-slot capacity and supported rank configurations per channel documented by the server vendor.
Some server platforms will auto-negotiate memory speed to a lower JEDEC profile if the BIOS does not explicitly support DDR5-6400 or if a mix of DIMM speeds/ranks is present. For predictable behavior, use matched sets and consult the server vendor’s Qualified Vendor List (QVL).
Mixing memory modules: best practices
Mixing DIMMs of different capacities, speeds, or vendors can cause the system to run at the slowest common denominator or lead to suboptimal memory timing. Recommended guidelines:
- Where possible, install matched modules (same part number, capacity, rank, and speed) across channels to maximize interleaving and stability.
- If mixing is unavoidable, ensure BIOS settings reflect the desired operating speed and test the configuration under representative loads.
- Observe vendor QVLs and use memory population rules (which slots to populate first) for the highest performance and stability.
Thermal design and power considerations
Power draw characteristics
DDR5 introduces power-management improvements but DDR5 RDIMMs at higher speeds such as 6400 MT/s can have higher overall power demands relative to lower-speed or consumer-class modules. System designers should consider:
- DIMM power per module and its contribution to total system power draw.
- Impact on INFRA power planning in dense rack deployments — multiple high-capacity RDIMMs per server can increase draw under sustained workloads.
- Voltage regulation and thermal provisioning for the DIMM area; check server vendor power/thermal guidance for populated memory configurations.
Heatsinks, airflow and layout
While RDIMMs often ship with low-profile heat spreaders or none at all (depending on the SKU), good chassis airflow is critical in racks with high DIMM population. Consider:
- Ensuring front-to-back airflow is unobstructed.
- Using server chassis with adequate fan control and thermal zones.
- Monitoring DIMM temperatures during stress tests and sustained operations to avoid thermal throttling or reduced longevity.
Security, compliance, and operational risk
Data protection and silent corruption prevention
ECC memory reduces the risk of silent data corruption and is often a requirement for compliance-driven workloads (financial systems, regulated environments). For sensitive workloads:
- Enforce ECC-enforced hardware across the fleet to meet data integrity policies.
- Combine ECC memory with end-to-end checksums (application and storage layers) for multi-tier protection.
Regulatory and environmental compliance
Confirm compliance markings and environmental certifications (RoHS, WEEE, and other applicable local standards) when procuring modules in regulated jurisdictions. Micron typically provides compliance documentation on request or through product datasheets.
Symptoms, diagnostics, and corrective actions
Common memory-related issues include POST errors, machine-check exceptions (MCEs), system hangs, and application-level crashes. Recommended diagnostic steps:
- Check system event logs and BIOS POST codes for memory-specific error descriptors.
- Reseat DIMMs and test modules singly to isolate failing units.
- Confirm that firmware and BIOS versions are current and that memory training sequences complete successfully at boot.
- Run vendor-recommended diagnostics and long-run stress tests to replicate and capture failure modes.
Maintaining a healthy memory pool
Proactive practices reduce downtime:
- Keep a controlled inventory of verified spare modules matching production SKUs.
- Log firmware and BIOS changes and tie them to performance baselines.
- Schedule periodic stability tests for critical hosts during maintenance windows.
Comparisons and alternatives within DDR5 server memory
Dual rank vs single rank, RDIMM vs LRDIMM
Choosing between rank and buffer types depends on the platform and workload:
- Dual Rank: Often delivers more capacity per DIMM and can improve throughput through rank interleaving at the cost of slightly higher access latency in isolated microbenchmarks.
- Single Rank: Typically slightly lower latency; useful in latency-critical, capacity-light builds.
- RDIMM (Registered): Good balance of cost, compatibility, and signal integrity for many server platforms.
- LRDIMM (Load-Reduced): Uses buffer chips to reduce electrical loading on memory buses and enables even higher per-slot capacities; ideal when maximum capacity is the priority but requires platform support.